Green Building and Eco-Friendly Homes
The Journey to Green Homes and Eco-Friendly Living
In a world grappling with environmental challenges, the call for sustainable living has never been more urgent. One significant avenue towards a greener future is the adoption of eco-friendly practices in home construction and design. Green building not only minimizes the environmental impact but also creates healthier living spaces. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the concept of green building, highlight examples of eco-friendly homes, delve into statistics that underscore its importance, and discuss the challenges individuals might face along the way.
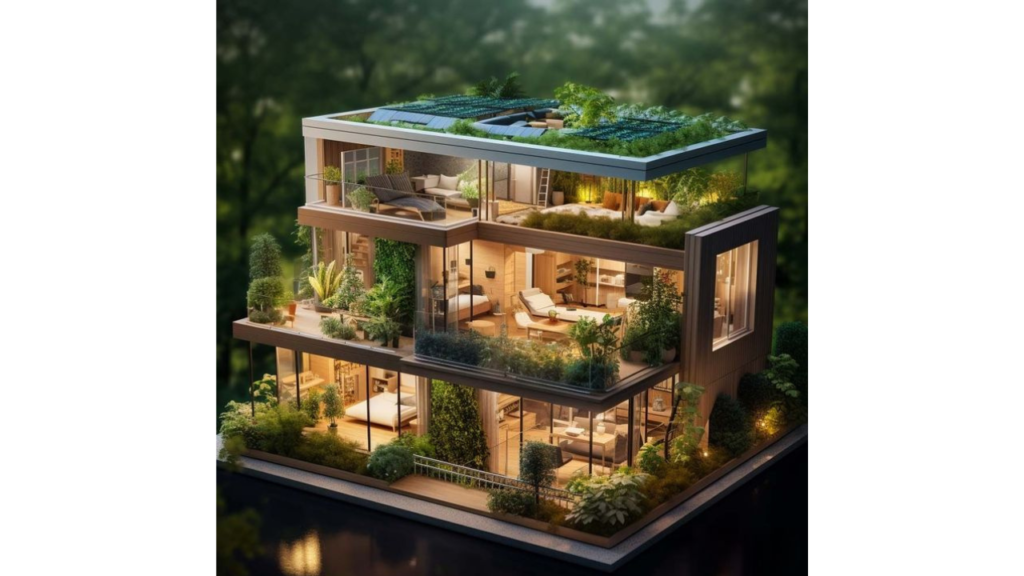

Understanding Green Building:
Green building is more than a trend; it’s a conscientious approach to construction that prioritizes environmental responsibility. Eco-friendly homes are designed to minimize resource consumption, reduce waste, and promote the use of renewable energy. These homes incorporate sustainable materials, energy-efficient technologies, and environmentally conscious practices to create a harmonious living space.
Table of Contents
Examples of Eco-Friendly Homes:
Passive Solar Design:
Passive Solar Design is a key component of green building and eco-friendly homes, focusing on harnessing the natural energy of the sun to create comfortable and energy-efficient living spaces. Unlike active solar systems that use external devices like solar panels, passive solar design relies on the strategic placement of windows, materials, and architectural elements to capture, store, and distribute solar energy within a building.
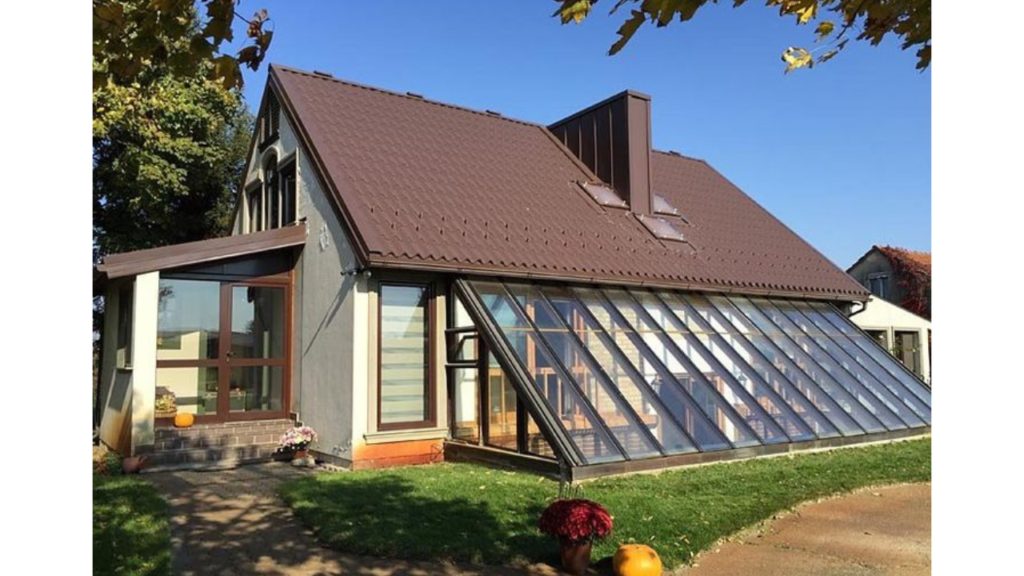

Here’s a brief overview of Passive Solar Design in the context of green building:
- Orientation and Placement:
- Passive solar design begins with the orientation of the building. Proper alignment allows for maximum exposure to the sun during the winter months and minimizes exposure during the summer.
- South-facing windows are prioritized to capture sunlight, while north-facing windows are minimized to reduce heat loss.
Optimal Window Placement:
- Well-placed windows act as “solar collectors” by allowing sunlight to enter the building. The design considers the angle of the sun at different times of the year to optimize natural lighting and warmth.
- Overhangs or shading devices are incorporated to block direct sunlight during the hottest parts of the day in summer, preventing overheating.
Thermal Mass:
- Thermal mass materials, such as concrete or tile floors and masonry walls, absorb and store heat from the sun during the day. They release this stored heat gradually during the night, providing a natural and energy-efficient form of heating.
- The balance of thermal mass and insulation is carefully considered to regulate temperature effectively.
Natural Ventilation:
- Passive solar design often integrates natural ventilation strategies to cool the building when needed. This may include strategically placed windows for cross-ventilation to encourage airflow and reduce the reliance on mechanical cooling systems.
Daylighting:
- Incorporating daylighting principles enhances the interior lighting of a home, reducing the need for artificial lighting during the day.
- It contributes to energy efficiency and the overall well-being of occupants by providing a connection to the outdoors.
Energy Efficiency:
- By utilizing the sun’s energy for heating and lighting, passive solar design reduces reliance on conventional heating and lighting systems, leading to significant energy savings.
- The overall energy efficiency of the building is improved, aligning with the principles of sustainability.
In summary, Passive Solar Design is a holistic approach that seamlessly integrates architectural elements with natural solar resources to create energy-efficient, comfortable, and environmentally friendly living spaces. It exemplifies the synergy between human habitation and the surrounding environment, making it a cornerstone of green building practices.
Net-Zero Energy Homes:
Net-Zero Energy Homes represent a cutting-edge approach to green building and eco-friendly homes, aiming to balance energy consumption with energy production, resulting in a net-zero energy footprint. The concept revolves around minimizing the energy demand of a home through efficiency measures and offsetting the remaining energy needs through the use of renewable sources. Here’s a brief breakdown of key elements:
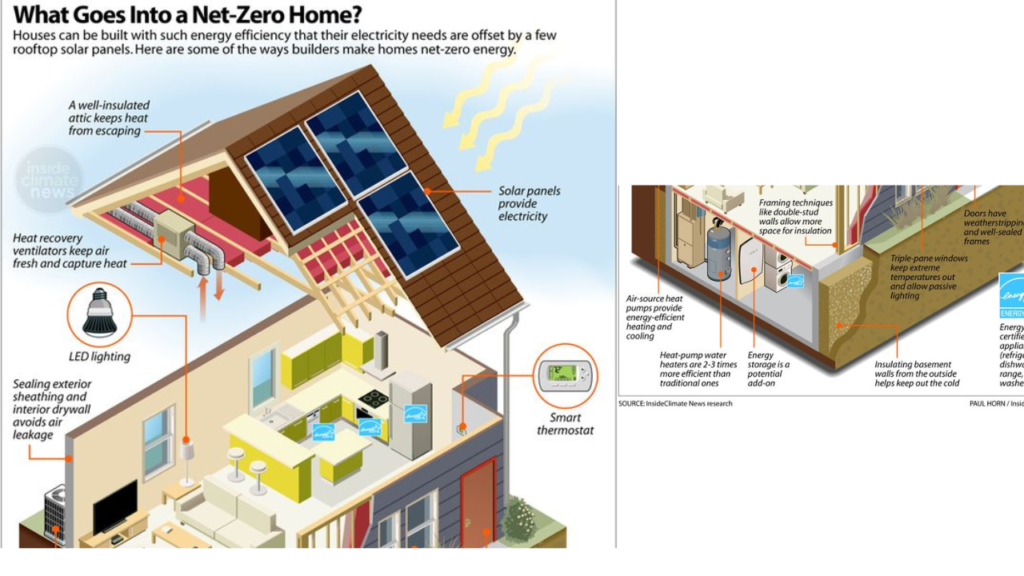
Energy Efficiency:
- Net-zero energy homes prioritize energy efficiency by incorporating advanced insulation, high-performance windows, and energy-efficient appliances.
- The design focuses on reducing energy consumption through efficient heating, cooling, and lighting systems.
Renewable Energy Sources:
- These homes integrate renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems to generate clean energy on-site.
- Solar panels, in particular, are a popular choice, converting sunlight into electricity and often producing surplus energy that can be fed back into the grid.
Energy Storage and Management:
- Energy storage systems, such as batteries, are often employed to store excess energy generated during periods of high production (e.g., sunny days) for use during times of low production or high demand.
- Smart energy management systems optimize energy use by controlling when and how energy is consumed, ensuring efficient utilization.
Monitoring and Control Systems:
- Net-zero homes typically incorporate advanced monitoring and control systems to track energy consumption and production in real-time.
- Homeowners can actively manage their energy usage and make informed decisions to further reduce their carbon footprint.
Holistic Design Approach:
- Net-zero energy homes take a holistic approach to design, considering factors like orientation, landscaping, and passive solar design to maximize natural heating and cooling opportunities.
- Integrating energy-efficient appliances and smart home technologies contributes to a comprehensive strategy for minimizing energy consumption.
Benefits of Net-Zero Energy Homes:
- Environmental Impact: By generating as much clean energy as they consume, these homes significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on non-renewable resources.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial investment may be higher, homeowners often experience long-term cost savings through reduced energy bills and, in some cases, government incentives.
- Energy Independence: Net-zero homes provide a level of energy independence, relying less on external energy sources and mitigating the impact of energy price fluctuations.
In the context of green building and eco-friendly homes, net-zero energy homes stand as a beacon of sustainable living. They demonstrate that it’s possible not only to minimize the environmental impact of residential structures but also to contribute positively to the energy grid and promote a more sustainable and resilient future.
Explore practical tips for achieving a zero-waste lifestyle and enhancing your commitment to sustainable living by visiting https://wecareearth.com/sustainable-living/zero-waste/ where you’ll find valuable insights aligned with the principles of green building and eco-friendly homes discussed in the paragraph above.
Green Roof Homes:
Green roof homes are a sustainable and eco-friendly building design concept that involves covering a building’s roof with vegetation, creating a living, breathing ecosystem. Also known as living roofs or vegetated roofs, green roof homes offer numerous environmental and energy-related benefits, making them a key component of green building and eco-friendly home initiatives.
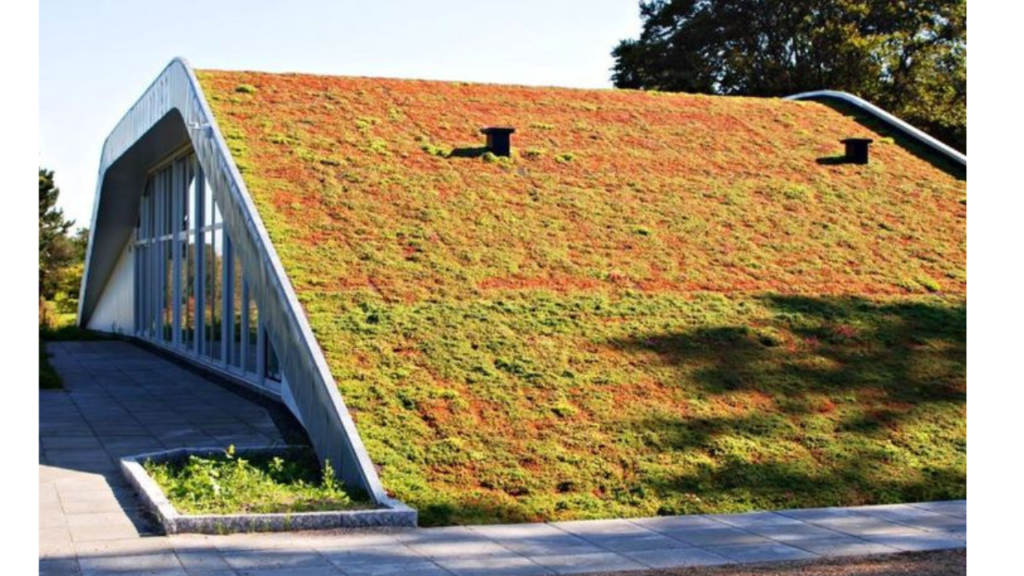

Key Features and Components:
Vegetation Layer:
- Green roofs consist of a layer of vegetation, which can include grasses, plants, or even small trees. These plants are specifically chosen for their ability to thrive in the rooftop environment.
Growing Medium:
- A specialized growing medium, often a lightweight soil or substrate, is used to support plant growth while minimizing the overall weight on the structure.
Drainage and Waterproofing Layers:
- To prevent water leakage and ensure proper drainage, green roofs typically include waterproofing layers and a drainage system. This prevents excess water from accumulating on the roof and causing structural issues.
Insulation:
- Green roofs provide natural insulation, reducing the energy needed for heating and cooling. The soil and vegetation act as a barrier, regulating indoor temperatures and reducing the urban heat island effect.
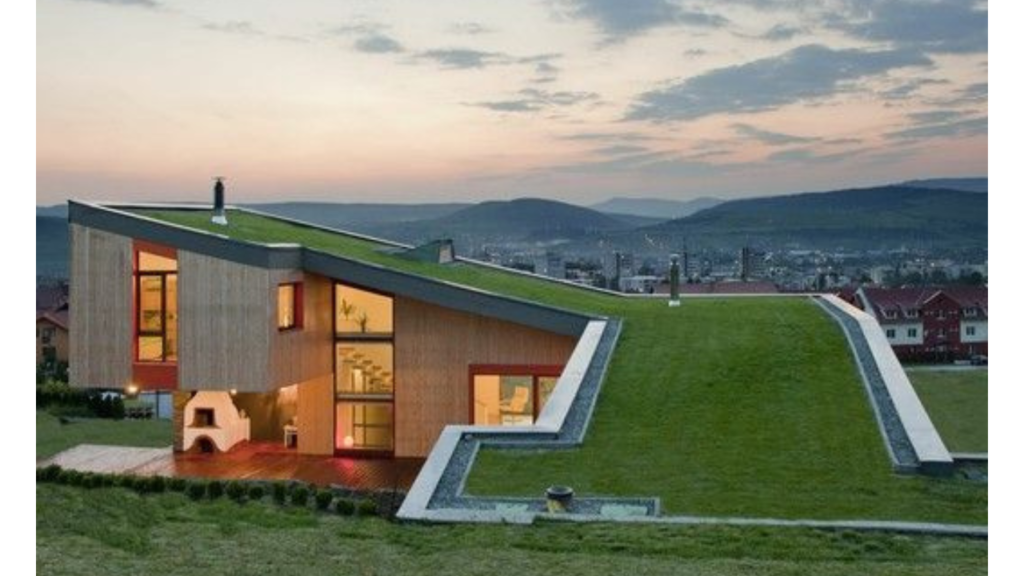

Environmental Benefits of Green House Homes:
Stormwater Management:
- Green roofs absorb and retain rainwater, preventing excessive runoff and reducing the strain on stormwater management systems. This helps mitigate the risk of flooding in urban areas.
Air Quality Improvement:
- The vegetation on green roofs contributes to air purification by capturing pollutants and particulate matter. This helps improve overall air quality, particularly in densely populated urban environments.
Biodiversity Enhancement:
- Green roofs create habitat opportunities for birds, insects, and other small animals, promoting urban biodiversity. This contributes to the overall health of ecosystems in urban areas.
Energy Efficiency:
- The insulation provided by green roofs reduces the need for artificial heating and cooling, leading to energy savings and a decreased carbon footprint. This makes green roof homes more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Benefits for Building Owners:
Extended Roof Lifespan:
- The layer of vegetation and soil protects the roof membrane from UV radiation and temperature extremes, extending the lifespan of the roof.
Aesthetic Appeal:
- Green roofs enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings, providing a visually pleasing and harmonious integration of nature into urban landscapes.
Property Value:
- Homes with green roofs may experience an increase in property value due to their sustainability features and energy efficiency.
In the context of green building and eco-friendly homes, green roof homes stand as an innovative solution that aligns with the principles of sustainability, resource efficiency, and environmental responsibility. As part of a holistic approach to green building, green roofs contribute to creating healthier, more resilient, and environmentally conscious living spaces.
Sustainable Materials:
Sustainable materials play a pivotal role in green building and the construction of eco-friendly homes. These materials are chosen for their minimal environmental impact, renewability, and energy efficiency. Here’s a brief overview of sustainable materials in the context of green building and eco-friendly homes:
Reclaimed Wood:
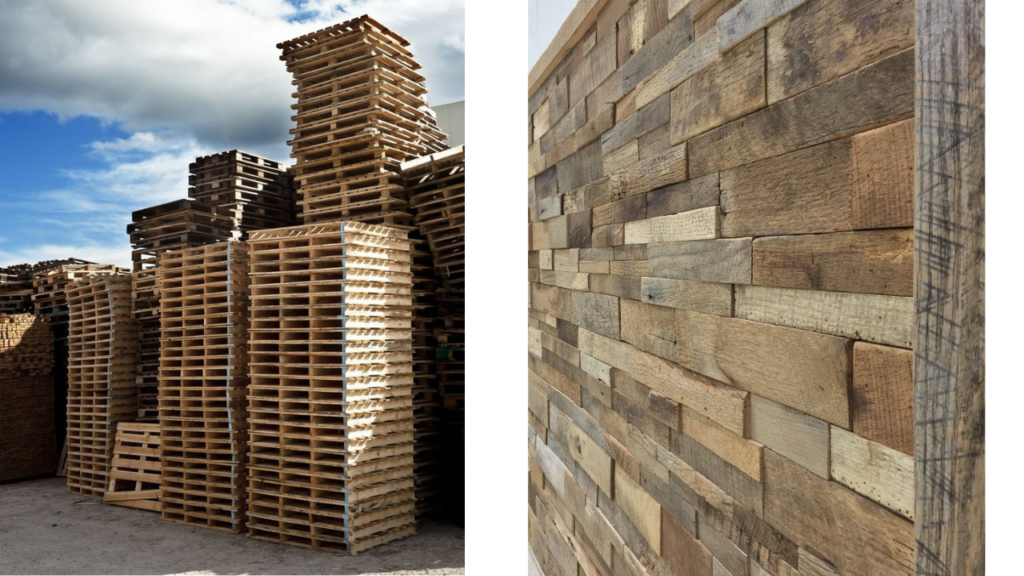

- Definition: Wood salvaged from old buildings, bridges, or other structures and repurposed for new construction.
- Sustainability Benefits: Reduces the demand for new timber, preserving forests and minimizing the environmental impact of logging.
Bamboo:

- Definition: A fast-growing grass that can be harvested for construction purposes.
- Sustainability Benefits: Rapid growth makes bamboo a highly renewable resource. It requires minimal pesticides and fertilizers compared to traditional hardwoods.
Recycled Steel:
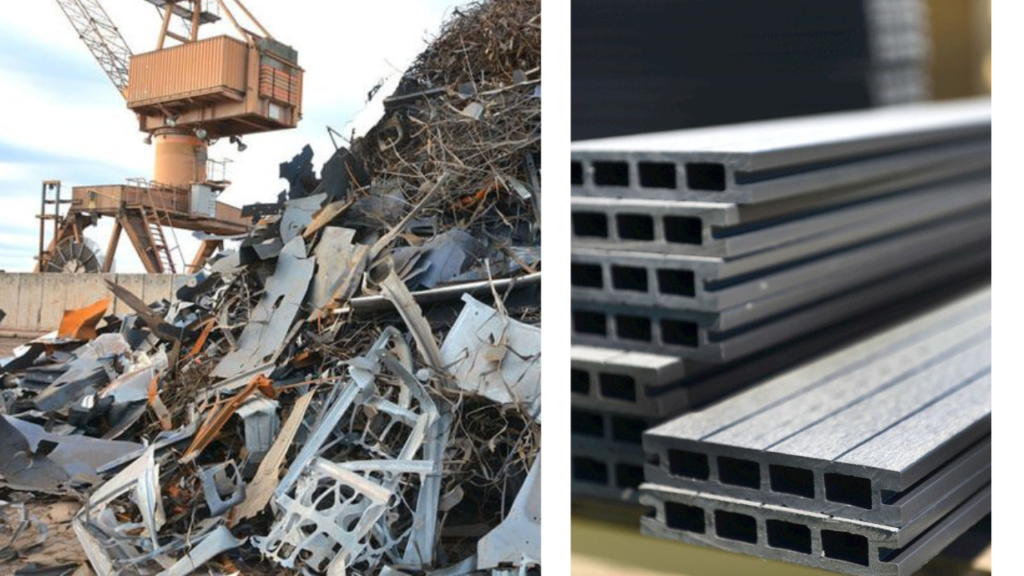

- Definition: Steel produced from recycled scrap metal rather than raw iron ore.
- Sustainability Benefits: Reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional steel production. Enhances the recyclability of materials.
Recycled Concrete:

- Definition: Crushed concrete from demolished structures repurposed for new construction.
- Sustainability Benefits: Diverts construction waste from landfills, conserves natural resources, and reduces the environmental impact of concrete production.
Fly Ash Concrete:

- Definition: Concrete incorporating fly ash, a byproduct of coal combustion.
- Sustainability Benefits: Reduces the need for cement, lowering carbon emissions associated with concrete production. Utilizes an industrial waste product.
Cork:

- Definition: Harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without causing harm to the trees.
- Sustainability Benefits: Renewable and biodegradable material. Cork forests contribute to biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
Recycled Glass:

- Definition: Glass cullet from recycled bottles and other glass products.
- Sustainability Benefits: Reduces the energy required for glass production and the need for raw materials. Diverts glass waste from landfills.
Straw Bales:

- Definition: Bales of straw used as building blocks in construction.
- Sustainability Benefits: A highly renewable agricultural byproduct. Provides excellent insulation and reduces the need for traditional construction materials.
Recycled Plastic:

- Definition: Plastics recycled from consumer and industrial waste.
- Sustainability Benefits: Reduces the environmental impact of plastic pollution. Provides an alternative to traditional construction materials.
Low VOC Paints and Finishes:

- Definition: Paints and finishes with low volatile organic compound (VOC) content.
- Sustainability Benefits: Improves indoor air quality by minimizing the release of harmful chemicals. Reduces the environmental impact of conventional paint products.
Utilizing sustainable materials in green building not only contributes to the overall environmental health but also sets a standard for responsible construction practices. The choice of materials is a key factor in creating homes that are energy-efficient, resource-conscious, and aligned with the principles of sustainable living.
Smart Homes for Energy Efficiency:
Smart Homes for Energy Efficiency play a pivotal role in the context of Green Building and Eco-Friendly Homes by integrating advanced technologies to optimize energy consumption and enhance overall efficiency. These homes leverage smart devices and systems to monitor, control, and automate various aspects of energy usage, promoting sustainability in the following ways:
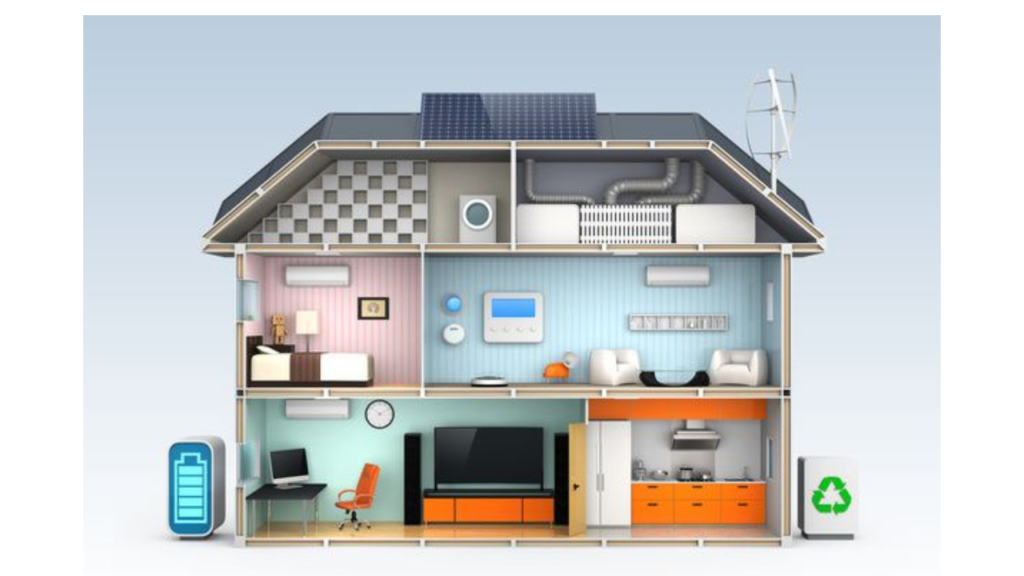

Energy Monitoring and Management:
- Smart homes are equipped with energy monitoring systems that track energy usage in real-time. Residents can gain insights into their consumption patterns and make informed decisions to minimize waste.
Smart Lighting and HVAC Systems:
- Intelligent lighting and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems adjust automatically based on occupancy, time of day, and environmental conditions. This ensures that energy is used only when necessary, reducing overall consumption.
Renewable Energy Integration:
- Smart homes often incorporate renewable energy sources such as solar panels. These systems can be integrated with smart grids to optimize the use of solar power and reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
Home Automation for Efficiency:
- Automation plays a key role in optimizing energy efficiency. Smart home platforms enable residents to control lighting, appliances, and thermostats remotely, ensuring that energy is not wasted when rooms are unoccupied.
Energy-Efficient Appliances and Devices:
- Smart homes feature energy-efficient appliances and devices that meet stringent standards for energy consumption. From smart thermostats to energy-star-rated appliances, these contribute to the overall sustainability of the home.
Adaptive Learning Systems:
- Some smart home technologies incorporate adaptive learning algorithms. Over time, these systems learn residents’ preferences and behaviors, adjusting settings automatically to maximize energy efficiency without sacrificing comfort.
Integration with Smart Grids:
- Smart homes can be connected to smart grids, allowing them to respond to real-time electricity pricing. This enables residents to schedule energy-intensive tasks during off-peak hours, reducing both costs and strain on the grid.
Water Conservation Measures:
- Smart homes extend their focus beyond energy to water conservation. Smart irrigation systems, leak detectors, and water usage monitoring contribute to a holistic approach to eco-friendly living.
In summary, the integration of smart technologies in eco-friendly homes amplifies the overall impact of green building practices. By harnessing the power of automation, data analytics, and renewable energy sources, smart homes for energy efficiency represent a modern and effective approach to sustainable living. This not only reduces the environmental footprint of homes but also provides residents with the tools to actively participate in the journey towards a greener and more energy-efficient future.
Statistics on Green Building:
To truly understand the impact of green building, let’s delve into some compelling statistics:
- According to the U.S. Green Building Council, green construction is expected to account for more than 3.3 million U.S. jobs by 2028.
- A study by the World Green Building Council found that green buildings can lead to a 15% reduction in water consumption and a 20% reduction in energy use compared to traditional buildings.
- The International Energy Agency states that the building and construction sector is responsible for approximately 36% of global final energy consumption and nearly 40% of total direct and indirect CO2 emissions.
Challenges in Adopting Green Building Practices:
While the benefits of green building are substantial, challenges may arise during the transition:
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost of incorporating green technologies and materials can be higher. However, it’s essential to consider the long-term savings in energy costs and environmental benefits.
- Limited Awareness: Many individuals are still unaware of the advantages of green building. Raising awareness and educating communities is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Regulatory Barriers: Some regions may lack supportive policies or incentives for green building. Advocacy for policy changes is essential for overcoming these barriers.
The Human Impact:
Embarking on the journey of green living goes beyond statistics and facts. It’s about the profound impact on individuals and their well-being. Adopting an eco-friendly lifestyle brings a sense of purpose and accomplishment. Living in a green home fosters a connection with nature and promotes a healthier lifestyle.
How You’ll Feel:
- Empowered: Taking control of your environmental footprint empowers you to contribute positively to the planet’s well-being.
- Healthier Living: Green homes often have superior indoor air quality, promoting better health and well-being.
- Connection to Nature: Living in a space designed with nature in mind fosters a sense of connection and appreciation for the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions.
What is green building, and how does it contribute to sustainability?
Green building is an approach to construction that prioritizes environmental responsibility and resource efficiency. It aims to minimize the impact on the environment throughout a building’s lifecycle, from design and construction to operation and eventual demolition. Green building incorporates sustainable materials, energy-efficient technologies, and eco-friendly practices to create healthier living spaces.
What are some key features of eco-friendly homes?
Eco-friendly homes incorporate several key features, including energy-efficient appliances, smart home technologies, renewable energy sources (such as solar panels), sustainable and recycled building materials, proper insulation for energy conservation, and water-saving fixtures. These features collectively contribute to a reduced environmental footprint and promote sustainable living.
How do smart homes contribute to energy efficiency in eco-friendly living?
Smart homes leverage advanced technologies to optimize energy consumption and enhance overall efficiency. Intelligent systems, such as smart lighting, HVAC controls, and energy monitoring devices, allow residents to manage and automate energy usage. This not only reduces waste but also promotes a more sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle.
Are there financial benefits to adopting green building practices?
Yes, adopting green building practices can lead to long-term financial benefits. While the initial upfront costs may be higher, energy-efficient features and sustainable practices often result in reduced utility bills over time. Additionally, some regions offer incentives, tax credits, or grants for green building initiatives, providing further financial motivation.
What are the environmental benefits of living in an eco-friendly home?
Eco-friendly homes contribute to environmental conservation by reducing energy consumption, minimizing water usage, and utilizing sustainable materials. This leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions, less strain on natural resources, and a smaller overall environmental footprint. Living in such homes helps support a healthier planet for current and future generations.
Are there challenges associated with adopting green building practices?
Yes, challenges include higher initial costs, limited awareness, and potential regulatory barriers. The initial investment in green technologies and materials can be a deterrent for some. Raising awareness about the benefits of green building and advocating for supportive policies are essential steps in overcoming these challenges.
How does green building contribute to job creation?
The green building sector creates jobs by fostering the demand for skilled professionals in areas such as sustainable design, renewable energy installation, energy auditing, and green construction practices. As the industry continues to grow, it generates employment opportunities and supports a workforce focused on environmental sustainability.
Can I retrofit my existing home to be more eco-friendly?
Yes, retrofitting an existing home is a viable option to make it more eco-friendly. This may involve adding insulation, upgrading windows, installing energy-efficient appliances, and incorporating smart home technologies. While the extent of retrofitting may vary, even small changes can contribute to a more sustainable living environment.
How does green building impact indoor air quality?
Green building practices prioritize indoor air quality by using non-toxic, low-emission materials and promoting proper ventilation. This focus on healthier indoor environments helps reduce the presence of harmful pollutants, fostering improved respiratory health and overall well-being for residents.
Are there certifications for green buildings, and why are they important?
Yes, certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) exist to evaluate and recognize sustainable building practices. These certifications provide a standardized way to assess the environmental performance of buildings, ensuring they meet established criteria for sustainability. They are important for both industry recognition and market value.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the shift towards green building and eco-friendly homes is a crucial step in our collective journey towards sustainability. By highlighting examples, presenting compelling statistics, and acknowledging the challenges, we hope to inspire individuals to consider the impact of their living spaces on the planet. The journey to green living is not without its hurdles, but the rewards—both for the Earth and the individual—are immeasurable. We invite you to explore and implement the practical tips we’ve shared.
For a comprehensive guide and additional resources, visit our main page at “WeCareEarth.com.” This hub serves as a central source of information, offering insights, tools, and community support to empower individuals in making significant strides toward reducing their environmental footprint.
To delve deeper into the sources that enriched the content of this blog post, you can explore the referenced URLs below, providing a comprehensive foundation for the information presented:
- U.S. Green Building Council. (https://www.usgbc.org/)
- World Green Building Council. (https://www.worldgbc.org/)
- International Energy Agency. (https://www.iea.org/)
These links serve as valuable resources, contributing to the credibility and depth of the discussed topics in the blog post.

6 Comments